For a full list of publications, check here.
104. Gerstner NC, McCann JT, Martin JG, Henn KM, Riske K, Anantakrishnan S, Graham TGW, Darzacq X, Miller EW. Bis(trifluoromethyl)carborhodamines: Highly Fluorogenic, Far-Red to Near-Infrared Dyes for Live Cell Fluorescence Microscopy, Activity-Based Sensing, and Single-Molecule Microscopy. J Am Chem Soc. 2025 Jun 25;147(25):21950-21960. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5c05473. Epub 2025 Jun 11. PubMed PMID: 40501037
103. Roy D, Michalet X, Miller EW, Bharadwaj K, Weiss S. Toward measurements of absolute membrane potential in Bacillus subtilis using fluorescence lifetime. Biophys Rep (N Y). 2025 Mar 12;5(1):100196. doi: 10.1016/j.bpr.2025.100196. Epub 2025 Jan 10. PubMed PMID: 39798601
102. Zhou X, Belavek KJ, Navarro MX, Martinez KN, Hinojosa A, Miller EW. Ratio-based indicators for cytosolic Ca(2+) with visible light excitation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Feb 18;122(7):e2410436122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2410436122. Epub 2025 Feb 12. PubMed PMID: 39937863
101. Roy D, Michalet X, Miller EW, Bharadwaj K, Weiss S. Towards measurements of absolute membrane potential in Bacillus subtilis using fluorescence lifetime. bioRxiv. 2024 Dec 21;. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.13.598880. PubMed PMID: 38915670
100. Wang B, Ma T, Chen T, Nguyen T, Crouse E, Fleming SJ, Walker AS, Valakh V, Nehme R, Miller EW, Farhi SL, Babadi M. Robust self-supervised denoising of voltage imaging data using CellMincer. Npj Imaging. 2024;2(1):51. doi: 10.1038/s44303-024-00055-x. Epub 2024 Dec 4. PubMed PMID: 39649342
99. Navarro MX, Gerstner NC, Lipman SM, Dolgonos GE, Miller EW. Improved Sensitivity in a Modified Berkeley Red Sensor of Transmembrane Potential. ACS Chem Biol. 2024 Oct 18;19(10):2214-2219. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.4c00442. Epub 2024 Oct 2. PubMed PMID: 39358835
98. Martinez KN, Gerstner NC, Yang SJ, Miller EW. Extended voltage imaging in cardiomyocytes with a triplet state quencher-stabilized silicon rhodamine. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2024 Sep 1;109:129842. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2024.129842. Epub 2024 Jun 4. PubMed PMID: 38844174
97. Hernández-Morales M, Morales-Weil K, Han SM, Han V, Tran T, Benner EJ, Pegram K, Meanor J, Miller EW, Kramer RH, Liu C. Electrophysiological Mechanisms and Validation of Ferritin-Based Magnetogenetics for Remote Control of Neurons. J Neurosci. 2024 Jul 24;44(30). doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1717-23.2024. PubMed PMID: 38777598
96. Turnbull JL, Miller EW. An open and shut case? Chemistry to control xanthene dyes. Trends Chem. 2024 Apr;6(4):164-172. doi: 10.1016/j.trechm.2024.01.006. Epub 2024 Apr 10. PubMed PMID: 39036609
95. Gest AMM, Lazzari-Dean JR, Ortiz G, Yaeger-Weiss SK, Boggess SC, Miller EW. A red-emitting carborhodamine for monitoring and measuring membrane potential. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Apr 2;121(14):e2315264121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2315264121. Epub 2024 Mar 29. PubMed PMID: 38551837
94. Gest AMM, Grenier V, Miller EW. Optical Estimation of Membrane Potential Values Using Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy and Hybrid Chemical-Genetic Voltage Indicators. Bioelectricity. 2024 Mar 1;6(1):34-41. doi: 10.1089/bioe.2023.0027. Epub 2024 Mar 15. PubMed PMID: 38516638
93. Zheng S, Dadina N, Mozumdar D, Lesiak L, Martinez KN, Miller EW, Schepartz A. Long-term super-resolution inner mitochondrial membrane imaging with a lipid probe. Nat Chem Biol. 2024 Jan;20(1):83-92. doi: 10.1038/s41589-023-01450-y. Epub 2023 Oct 19. PubMed PMID: 37857992
92. Turnbull JL, Golden RP, Benlian BR, Henn KM, Lipman SM, Miller EW. Mild and scalable synthesis of phosphonorhodamines. Chem Sci. 2023 Oct 25;14(41):11365-11373. doi: 10.1039/d3sc02590j. eCollection 2023 Oct 25. PubMed PMID: 37886078
91. Hanč P, Gonzalez RJ, Mazo IB, Wang Y, Lambert T, Ortiz G, Miller EW, von Andrian UH. Multimodal control of dendritic cell functions by nociceptors. Science. 2023 Mar 31;379(6639):eabm5658. doi: 10.1126/science.abm5658. Epub 2023 Mar 31. PubMed PMID: 36996219.
90. Kirk MJ, Gold A, Ravi A, Sterne GR, Scott K, Miller EW. Cell-Surface Targeting of Fluorophores in Drosophila for Rapid Neuroanatomy Visualization. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2023 Mar 1;14(5):909-916. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.2c00745. Epub 2023 Feb 17. PubMed PMID: 36799505; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC10187464.
89. Raliski BK, Mun DM, Miller EW. Sulfone Rhodamines for Voltage Imaging. Chem Asian J. 2022 Dec 14;17(24):e202200906. doi: 10.1002/asia.202200906. Epub 2022 Nov 10. PubMed PMID: 36356288; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC9772261.
88. Klier PEZ, Roo R, Miller EW. Fluorescent indicators for imaging membrane potential of organelles. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2022 Dec;71:102203. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2022.102203. Epub 2022 Sep 6. Review. PubMed PMID: 36084425.
87. Yang S, Yamazaki S, Cox KH, Huang YL, Miller EW, Takahashi JS. Coupling-dependent metabolic ultradian rhythms in confluent cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Nov 8;119(45):e2211142119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2211142119. Epub 2022 Nov 2. PubMed PMID: 36322771; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC9659342.
86. Zhou X, Fang Y, Wimalasiri V, Stains CI, Miller EW. A long-wavelength xanthene dye for photoacoustic imaging. Chem Commun (Camb). 2022 Oct 25;58(85):11941-11944. doi: 10.1039/d2cc03947h. PubMed PMID: 36196957; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC9634815.
85. McCann JT, Benlian BR, Yaeger-Weiss SK, Knudson IJ, He M, Miller EW. Flipping the Switch: Reverse-Demand Voltage-Sensitive Fluorophores. J Am Chem Soc. 2022 Jul 27;144(29):13050-13054. doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c05385. Epub 2022 Jul 14. PubMed PMID: 35834763; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC9462387.
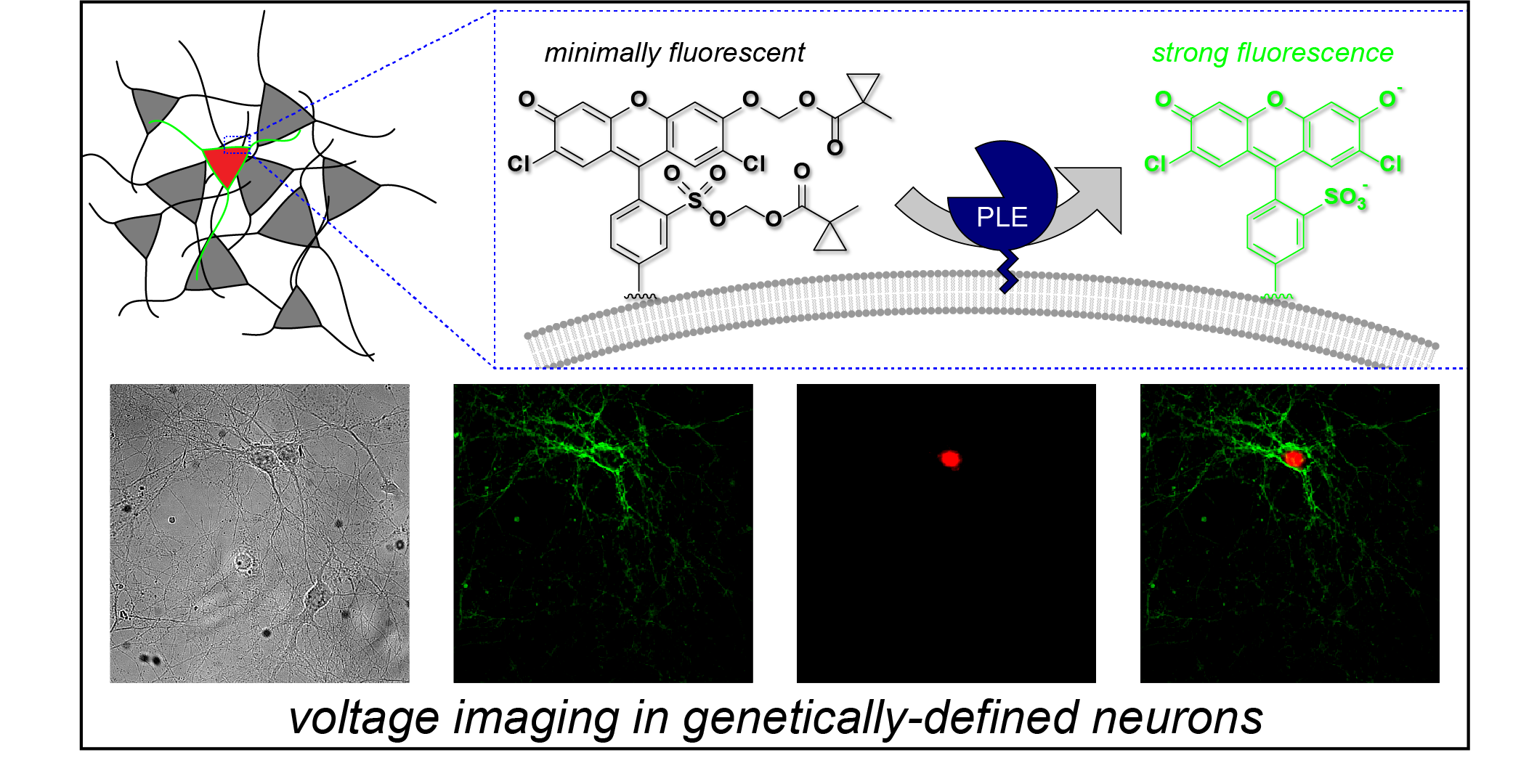
84. Klier PEZ, Gest AMM, Martin JG, Roo R, Navarro MX, Lesiak L, Deal PE, Dadina N, Tyson J, Schepartz A, Miller EW. Bioorthogonal, Fluorogenic Targeting of Voltage-Sensitive Fluorophores for Visualizing Membrane Potential Dynamics in Cellular Organelles. J Am Chem Soc. 2022 Jul 13;144(27):12138-12146. doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c02664. Epub 2022 Jul 1. PubMed PMID: 35776693; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC9433336.
83. Yudovich S, Marzouqe A, Kantorovitsch J, Teblum E, Chen T, Enderlein J, Miller EW, Weiss S. Electrically controlling and optically observing the membrane potential of supported lipid bilayers. Biophys J. 2022 Jul 5;121(13):2624-2637. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2022.05.037. Epub 2022 May 25. PubMed PMID: 35619563; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC9300657.
82. Abdelfattah AS, Ahuja S, Akkin T, Allu SR, Brake J, Boas DA, Buckley EM, Campbell RE, Chen AI, Cheng X, Čižmár T, Costantini I, De Vittorio M, Devor A, Doran PR, El Khatib M, Emiliani V, Fomin-Thunemann N, Fainman Y, Fernandez-Alfonso T, Ferri CGL, Gilad A, Han X, Harris A, Hillman EMC, Hochgeschwender U, Holt MG, Ji N, Kılıç K, Lake EMR, Li L, Li T, Mächler P, Miller EW, Mesquita RC, Nadella KMNS, Nägerl UV, Nasu Y, Nimmerjahn A, Ondráčková P, Pavone FS, Perez Campos C, Peterka DS, Pisano F, Pisanello F, Puppo F, Sabatini BL, Sadegh S, Sakadzic S, Shoham S, Shroff SN, Silver RA, Sims RR, Smith SL, Srinivasan VJ, Thunemann M, Tian L, Tian L, Troxler T, Valera A, Vaziri A, Vinogradov SA, Vitale F, Wang LV, Uhlířová H, Xu C, Yang C, Yang MH, Yellen G, Yizhar O, Zhao Y. Neurophotonic tools for microscopic measurements and manipulation: status report. Neurophotonics. 2022 Jan;9(Suppl 1):013001. doi: 10.1117/1.NPh.9.S1.013001. Epub 2022 Apr 27. PubMed PMID: 35493335; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC9047450.
81. Moreno JD, Bhagavan D, Li A, Gerstner NC, Miller EW, Huebsch N, Cresci S, Silva JR. Pulsus Alternans in Cardiogenic Shock Recapitulated in Single Cell Fluorescence Imaging of a Patient's Cardiomyocyte. Circ Heart Fail. 2022 Feb;15(2):e008855. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.121.008855. Epub 2021 Dec 10. PubMed PMID: 34886677; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC8847329.
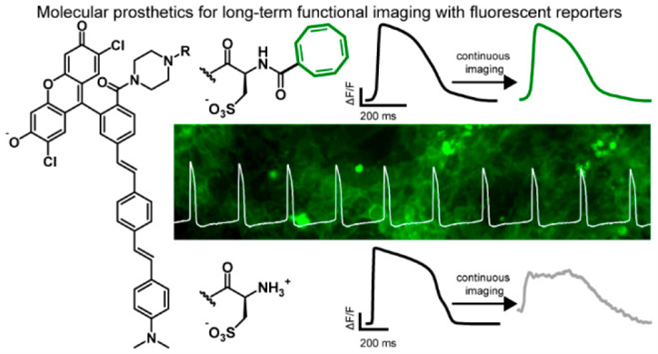
80. Grenier V, Martinez KN, Benlian BR, García-Almedina DM, Raliski BK, Boggess SC, Maza JC, Yang SJ, Gest AMM, Miller EW. Molecular Prosthetics for Long-Term Functional Imaging with Fluorescent Reporters. ACS Cent Sci. 2022 Jan 26;8(1):118-121. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.1c01153. Epub 2022 Jan 13. PubMed PMID: 35111902; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC8802189.
79. Kierzek M, Deal PE, Miller EW, Mukherjee S, Wachten D, Baumann A, Kaupp UB, Strünker T, Brenker C. Simultaneous recording of multiple cellular signaling events by frequency- and spectrally-tuned multiplexing of fluorescent probes. Elife. 2021 Dec 3;10. doi: 10.7554/eLife.63129. PubMed PMID: 34859780; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC8700268.
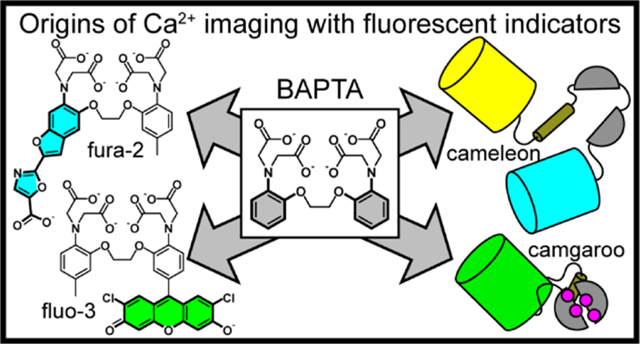
78. Zhou X, Belavek KJ, Miller EW. Origins of Ca2+ Imaging with Fluorescent Indicators. Biochemistry. 2021 Nov 23;60(46):3547-3554. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.1c00350. Epub 2021 Jul 12. PubMed PMID: 34251789; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC8612960.
77. Kirk MJ, Benlian BR, Han Y, Gold A, Ravi A, Deal PE, Molina RS, Drobizhev M, Dickman D, Scott K, Miller EW. Voltage Imaging in Drosophila Using a Hybrid Chemical-Genetic Rhodamine Voltage Reporter. Front Neurosci. 2021;15:754027. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.754027. eCollection 2021. PubMed PMID: 34867164; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC8637050.
76. Lazzari-Dean JR, Miller EW. Optical Estimation of Absolute Membrane Potential Using One- and Two-Photon Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy. Bioelectricity. 2021 Sep 1;3(3):197-203. doi: 10.1089/bioe.2021.0007. Epub 2021 Sep 9. PubMed PMID: 34734167; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC8558063.
75. Boggess SC, Gandhi SS, Benlian BR, Miller EW. Vinyl-Fluorene Molecular Wires for Voltage Imaging with Enhanced Sensitivity and Reduced Phototoxicity. J Am Chem Soc. 2021 Aug 11;143(31):11903-11907. doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c04543. Epub 2021 Jul 29. PubMed PMID: 34323478; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC8363594.
74. Charrez B, Charwat V, Siemons BA, Goswami I, Sakolish C, Luo YS, Finsberg H, Edwards AG, Miller EW, Rusyn I, Healy KE. Heart Muscle Microphysiological System for Cardiac Liability Prediction of Repurposed COVID-19 Therapeutics. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:684252. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.684252. eCollection 2021. PubMed PMID: 34421592; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC8378272.
73. Benlian BR, Klier PEZ, Martinez KN, Schwinn MK, Kirkland TA, Miller EW. Small Molecule-Protein Hybrid for Voltage Imaging via Quenching of Bioluminescence. ACS Sens. 2021 May 28;6(5):1857-1863. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.1c00058. Epub 2021 Mar 16. PubMed PMID: 33723996; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC8327619.
72. Puppo F, Sadegh S, Trujillo CA, Thunemann M, Campbell EP, Vandenberghe M, Shan X, Akkouh IA, Miller EW, Bloodgood BL, Silva GA, Dale AM, Einevoll GT, Djurovic S, Andreassen OA, Muotri AR, Devor A. All-Optical Electrophysiology in hiPSC-Derived Neurons With Synthetic Voltage Sensors. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021;15:671549. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.671549. eCollection 2021. PubMed PMID: 34122014; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC8193062.
71. Walker AS, Raliski BK, Nguyen DV, Zhang P, Sanders K, Karbasi K, Miller EW. Imaging Voltage in Complete Neuronal Networks Within Patterned Microislands Reveals Preferential Wiring of Excitatory Hippocampal Neurons. Front Neurosci. 2021;15:643868. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.643868. eCollection 2021. PubMed PMID: 34054406; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC8155642.
70. Walker AS, Raliski BK, Karbasi K, Zhang P, Sanders K, Miller EW. Optical Spike Detection and Connectivity Analysis With a Far-Red Voltage-Sensitive Fluorophore Reveals Changes to Network Connectivity in Development and Disease. Front Neurosci. 2021;15:643859. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.643859. eCollection 2021. PubMed PMID: 34054405; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC8155641.
69. Lee-Montiel FT, Laemmle A, Charwat V, Dumont L, Lee CS, Huebsch N, Okochi H, Hancock MJ, Siemons B, Boggess SC, Goswami I, Miller EW, Willenbring H, Healy KE. Integrated Isogenic Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Based Liver and Heart Microphysiological Systems Predict Unsafe Drug-Drug Interaction. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:667010. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.667010. eCollection 2021. PubMed PMID: 34025426; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC8138446.
68. Lazzari-Dean JR, Gest AMM, Miller EW. Measuring Absolute Membrane Potential Across Space and Time. Annu Rev Biophys. 2021 May 6;50:447-468. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-062920-063555. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Review. PubMed PMID: 33651949; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC8327616.
67. Charrez B, Charwat V, Siemons B, Finsberg H, Miller EW, Edwards AG, Healy KE. In vitro safety "clinical trial" of the cardiac liability of drug polytherapy. Clin Transl Sci. 2021 May;14(3):1155-1165. doi: 10.1111/cts.13038. Epub 2021 May 3. PubMed PMID: 33786981; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC8212738.
66. Turnbull JL, Benlian BR, Golden RP, Miller EW. Phosphonofluoresceins: Synthesis, Spectroscopy, and Applications. J Am Chem Soc. 2021 Apr 28;143(16):6194-6201. doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c01139. Epub 2021 Apr 2. PubMed PMID: 33797899; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC8327618.
65. Gest AMM, Yaeger-Weiss SK, Lazzari-Dean JR, Miller EW. VoltageFluor dyes and fluorescence lifetime imaging for optical measurement of membrane potential. Methods Enzymol. 2021;653:267-293. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2021.02.009. Epub 2021 Mar 29. PubMed PMID: 34099175; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC8356362.
64. Klier PEZ, Martin JG, Miller EW. Imaging Reversible Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Dynamics with a Masked Rhodamine Voltage Reporter. J Am Chem Soc. 2021 Mar 24;143(11):4095-4099. doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c13110. Epub 2021 Mar 12. PubMed PMID: 33710896; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC8015667.
63. Raliski BK, Kirk MJ, Miller EW. Imaging Spontaneous Neuronal Activity with Voltage-Sensitive Dyes. Curr Protoc. 2021 Mar;1(3):e48. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.48. PubMed PMID: 33760396; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC8363026.
62. Boggess SC, Lazzari-Dean JR, Raliski BK, Mun DM, Li AY, Turnbull JL, Miller EW. Fluorescence lifetime predicts performance of voltage sensitive fluorophores in cardiomyocytes and neurons. RSC Chem Biol. 2021 Feb 1;2(1):248-258. doi: 10.1039/d0cb00152j. Epub 2020 Dec 11. PubMed PMID: 34212146; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC8240514.
61. Ojala KS, Ginebaugh SP, Wu M, Miller EW, Ortiz G, Covarrubias M, Meriney SD. A high-affinity, partial antagonist effect of 3,4-diaminopyridine mediates action potential broadening and enhancement of transmitter release at NMJs. J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100302. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100302. Epub 2021 Jan 17. PubMed PMID: 33465376; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC7949096.
60. Ortiz, G.; Liu, P.; Deal, P. E.; Nensel, A. K.; Martinez, K. N.; Shamardani, K.; Adesnik, H.; Miller, E. W.; A Silicon-Rhodamine Chemical-Genetic Hybrid for Far Red Voltage Imaging from Defined Neurons in Brain Slice. RSC Chem Biol. 2021, 2, 1594-1599. DOI: 10.1039/d1cb00156f. [html]
59. Kulkarni, R. U.; Gest, A. M. M.; Lam, C. K.; Raliski, B. K.; James, F.; Adil, M. M.; Schaffer, D. V.; Wang, Y.; Miller, E. W. Computationally Assisted Design of High Signal-to-Noise Photoinduced Electron Transfer-Based Voltage-Sensitive Dyes. ChemRxiv. Preprint. DOI: 10.26434/chemrxiv.12401753.v1. [html]
58. Lee S.; Chung, C. Y.; Liu, P.; Craciun, L.; Nishikawa, Y.; Bruemmer, K. J.; Hamachi, I.; Saijo, K.; Miller, E. W.; Chang, C. J. Activity-Based Sensing with a Metal-Directed Acyl Imidazole Strategy Reveals Cell Type-Dependent Pools of Labile Brain Copper. J Am Chem Soc. 2020, 142, 14993-15003. DOI: 10.1021/jacs.0c05727. [pdf] [html]
57. Klimas, A.; Ortiz, G.; Boggess, S. C.; Miller, E. W.; Entcheva, E. Multimodal on-axis platform for all-optical electrophysiology with near-infrared probes in human stem-cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2020, 154, 62-70. DOI: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2019.02.004. [pdf] [html]
56. Ginebaugh, S. P.; Cyphers, E. D.; Lanka, V.; Ortiz, G.; Miller, E. W.; Laghaei, R.; Meriney, S. D. The Frog Motor Nerve Terminal Has Very Brief Action Potentials and Three Electrical Regions Predicted to Differentially Control Transmitter Release. J Neurosci. 2020, 40, 3504-16. DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2415-19.2020. [pdf] [html]
55. Kand, D.; Liu, P.; Navarro, M. X.; Fischer, L. J.; Rousso-Noori, L.; Friedmann-Morvinski, D.; Winter, A. H.; Miller, E. W.; Weinstain, R. Water-Soluble BODIPY Photocages with Tunable Cellular Localization. J Am Chem Soc 2020, 142, 4970-4. DOI: 10.1021/jacs.9b13219. [pdf] [html]
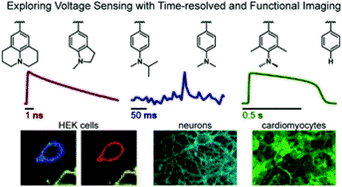
54. Liu, P.; Miller, E. W.; Electrophysiology, Unplugged: Imaging Membrane Potential with Fluorescent Indicators. Acc Chem Res 2020, 53, 11-19. DOI: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00514. [pdf] [html]
51. Lazzari-Dean, J. R.; Gest, A. M. M.; Miller, E. W.; Optical estimation of absolute membrane potential using fluorescence lifetime imaging. eLife. 2019, 8, e44522. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.44522. [pdf] [html]
FEATURED AS an elife digest.
50. Ohata, J.; Krishnamoorthy, L.; Gonzalez, M. A.; Xiao, T.; Iovan, D. A.; Toste, F. D.; Miller, E. W.; Chang, C. J.; An Activity-Based Methionine Bioconjugation Approach to Developing Proximity-Activated Imaging Reporters. ACS Central Science. 2020, 6, 32-40. [pdf] [html]
49. Franke, J. M.; Raliski, B. K.; Boggess, S. C.; Natesan, D. V.; Koretsky, E. T.; Zhang, P.; Kulkarni, R. U.; Deal, P. E.; Miller, E. W.; BODIPY fluorophores for membrane potential imaging. J Am Chem Soc. 2019, 141, 12824-31. DOI: 10.1021/jacs.9b05912. [pdf] [html]
48. Huebsch, N.; Charrez, B.; Siemons, B. A.; Boggess, S. C.; Wall, S.; Charwat, V.; Jaeger, K.; Montiel, F. L. T.; Jeffreys, N. C.; Deveshwar, N.; Edwards, A.; Serrano, J.; Snuderl, M.; Stahl, A.; Tveito, A.; Miller, E. W.; Healy, K. E.; Metabollically-driven maturation of hiPSC-cell derived heart-on-a-chip. bioRxiv. 2018, Preprint: DOI: 10.1101/485169. [pdf] [html]
47. Kazemipour, A.; Novak, O.; Flickinger, D.; Marvin, J. S.; Abdelfattah, A.; King, J.; Borden, P; Kim, J. J.; Deal, P.E.; Al-Abdullatif, S. H.; Miller, E. W.; Schreiter, E. R.; Druckmann, S.; Svoboda, K.; Looger, L. L.; Podgorski, K.; Kilohertz frame-rate two photon tomography. Nat Methods 2019, 16, 778-86. DOI: 10.1038/s41592-019-0493-9. [pdf] [html]
46. Park, J.; Kuo, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, Y. L.; Miller, E. W.; Weiss, S.; Improved surface functionalization and characterization of membrane targeted semiconductor voltage nanosensors. J Phys Chem Lett 2019, 10, 3906 – 13. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.9b01258. [pdf] [html]
44. Hamzeh, H.; Alvarez, L.; Strunker, T.; Kierzek, M.; Brenker, C.; Deal, P. E.; Miller, E. W.; Seifert, R.; Kaupp, U. B.; Kinetic and photonic techniques to study chemotactic signaling in sea urchin sperm. Methods Cell Biol. 2019, 151, 487-517. DOI: 10.1016/bs.mcb.2018.12.001. [pdf] [html]
43. Klimas, A.; Ortiz, G.; Boggess, S. C.; Miller, E. W.; Entcheva, E.; Multimodal on-axis platform for all-optical electrophysiology with near-infrared probes in human stem-cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2019, pii, S0079-6107(18)30279-7. DOI: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2019.02.004. [pdf] [html]
42. Boggess, S. C.; Gandhi, S. S.; Siemons, B. A.; Huebsch, N.; Healy, K. E.; Miller, E. W.; New Molecular Scaffolds for Fluorescent Voltage Indicators. ACS Chem Biol. 2019, 14, 390-396. DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.8b00978. [pdf] [html]
FEATURED "IN this issue" of THE March 2019 ISSUE OF ACS CHEMICAL BIOLOGY. [HTML]
39. McNamara H. M.; Dodson, S.; Huang, Y. L.; Miller, E. W.; Sandstede, B.; Cohen, A. E.; Geometry-Dependent Arrhythmias in Electrically Excitable Tissues. Cell Syst., 2018, 7, 359-370.e6. DOI: 10.1016/j.cels.2018.08.013. [pdf] [html]
38. Adil, M. M.; Gaj, T.; Rao, A. T.; Kulkarni, R. U.; Fuentes, C. M.; Ramadoss, G. N.; Ekman, F. K.; Miller, E. W.; Schaffer, D. V.; hPSC-Derived Striatal Cells Generated Using a Scalable 3D Hydrogel Promote Recovery in a Huntington Disease Mouse Model. Stem Cell Reports, 2018, 10, 1481. DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2018.03.007. [pdf] [html]
37. Contractor, A. A. and Miller, E. W.; Imaging Ca2+ with a Fluorescent Rhodol. Biochemistry, 2018, 57, 237-40. DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochm.7b01050. [pdf] [html]
35. McKeithan, W. L.; Savchenko, A; Yu, M. S.; Cerignoli, F.; Bruyneel, A. A. N.; Price, J. H.; Colas, A. R.; Miller, E. W.; Cashman, J. R.; Mercola, M.; An Automated Platform for Assessment of Congenital and Drug-Induced Arrhythmia with hiPSC-Derived Cardiomyocytes. Front Physiol 2017, 8, 766. DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00766. [pdf] [html]
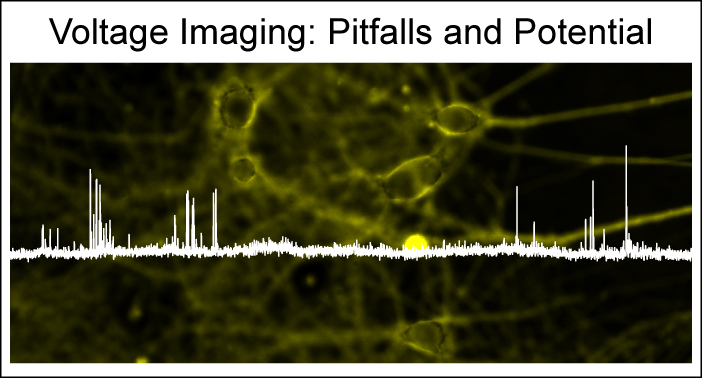
34. Kulkarni, R. U.; Miller, E. W.; "Voltage Imaging: Pitfalls and Potential." Biochemistry, 2017, 56, 5171-7. DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.7b00490 [pdf] [html]
33. Rodrigues, G. M. C.; Gaj, T.; Adil, M. M.; Wahba, J.; Rao, A. T.; Lorbeer, F. K.; Kulkarni, R. U.; Diogo, M. M.; Cabral, J. M. S.; Miller, E. W.; Hockemeyer, D.; Schaffer, D. V., "Defined and Scalable Differentiation of Human Oligodendrocyte Precursors from Pluripotent Stem Cells in a 3D Culture System" Stem Cell Reports, 2017, 8, 1770-83. DOI: 2017.10.1016/j.stemcr.2017.04.027 [pdf] [html]
32. Adil, M. M.; Vazin, T.; Ananthanarayanan B.; Rodrigues, G. M. C.; Rao, A. T.; Kulkarni, R. U.; Miller, E. W.; Kumar, S.; Schaffer, D. V.; "Engineered hydrogels increase the post-transplantation survival of encapsulated hESC-derived midbrain dopaminergic neurons," Biomaterials, 2017, 136, 1-11. DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.05.008. [pdf] [html]
31. *Knight, A. S.; *Kulkarni, R. U.; Zhou, E. Y.; Franke, J. M.; Miller, E. W.; Francis, M. B.; "A modular platform to develop peptoid-based selective fluorescent metal sensors," Chem Commun, 2017, 53, 3477-80. DOI: 10.1039/c7cc00931c. [pdf] [html]
30. *Kulkarni, R. U.; *Kramer, D. J.; Pourmandi, N.; Karbasi, K.; Bateup, H. S.; Miller, E. W.; “Voltage-sensitive rhodol with enhanced two-photon brightness,” Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2017, 114 (11), 2813-8. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1610791114. [pdf] [html]
Featured as a "Spotlight" in the April 2017 issue of ACS Chemical Biology. [html]
29. Adil, M. M.; Rodrigues, G. M. C.; Kulkarni, R. U.; Rao, A. T.; Chernavsky, N. E.; Miller, E. W.; Schaffer, D. V.; "Efficient generation of hPSC-derived midbrain dopaminergic neurons in a fully defined, scalable, 3D biomaterial platform." Sci Reports 2017, 7, 40573. DOI: 10.1038/srep40573. [pdf] [html]
28. Kulkarni, R. U.; Yin, H.; Pourmandi, N.; James, F.; Adil, M. M.; Schaffer, D. V.; Wang, Y.; Miller, E. W.; “A Rationally Designed, General Strategy for Membrane Orientation of Photoinduced Electron Transfer-Based Voltage-Sensitive Dyes.” ACS Chem Biol 2017, 12 (2), 407-13. DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.6b00981. [pdf] [html]
26. Miller, E. W ., Small molecule fluorescent voltage indicators for studying membrane potential. Curr Opin Chem Biol, 2016, 33, 74-80. DOI: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2016.06.003. [pdf] [html]
20. Dolensek, J.; Stozer, A.; Skelin Klemen, M.; Miller, E. W.; Slak Rupnik, M., The relationship between membrane potential and calcium dynamics in glucose-stimulated beta cell syncytium in acute mouse pancreas tissue slices. PLoS One 2013, 8, e82374. [pdf] [html]
19. Moshtagh-Khorasani, M.; Miller, E. W.; Torre, V., The spontaneous electrical activity of neurons in leech ganglia. Physiol Rep 2013, 1, e00089. [pdf] [html]
18. Miller, E. W.; Lin, J. Y.; Frady, E. P.; Steinbach, P. A.; Kristan, W. B.; Tsien, R. Y., Optically monitoring voltage in neurons by photo-induced electron transfer through molecular wires. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2012, 109 (6), 2114-2119. [pdf] [html]
17. Dodani, S. C.; Domaille, D. W.; Nam, C. I.; Miller, E. W.; Finney, L. A.; Vogt, S.; Chang, C. J., Calcium-dependent copper redistributions in neuronal cells revealed by a fluorescent copper sensor and X-ray fluorescence microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011, 108 (15), 5980-5. [pdf] [html]
16. Miller, E. W.; Taulet, N.; Onak, C. S.; New, E. J.; Lanselle, J. K.; Smelick, G. S.; Chang, C. J., Light-Activated Regulation of Cofilin Dynamics Using a Photocaged Hydrogen Peroxide Generator. J Am Chem Soc 2010. [pdf] [html]
15. Miller, E. W.; Dickinson, B. C.; Chang, C. J., Aquaporin-3 mediates hydrogen peroxide uptake to regulate downstream intracellular signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010, 107 (36), 15681-6. [pdf] [html]
14. Cheng, W. Y.; Tong, H.; Miller, E. W.; Chang, C. J.; Remington, J.; Zucker, R. M.; Bromberg, P. A.; Samet, J. M.; Hofer, T. P., An integrated imaging approach to the study of oxidative stress generation by mitochondrial dysfunction in living cells. Environ Health Perspect 2010, 118 (7), 902-8. [pdf]
13. Bao, L.; Avshalumov, M. V.; Patel, J. C.; Lee, C. R.; Miller, E. W.; Chang, C. J.; Rice, M. E., Mitochondria are the source of hydrogen peroxide for dynamic brain-cell signaling. J Neurosci 2009, 29 (28), 9002-10. [pdf] [html]
12. Srikun, D.; Miller, E. W.; Domaille, D. W.; Chang, C. J., An ICT-based approach to ratiometric fluorescence imaging of hydrogen peroxide produced in living cells. J Am Chem Soc 2008, 130 (14), 4596-7. [pdf] [html]
11. Miller, E. W.; He, Q.; Chang, C. J., Preparation and use of Leadfluor-1, a synthetic fluorophore for live-cell lead imaging. Nat Protoc 2008, 3 (5), 777-83. [pdf] [html]
10. Albers, A. E.; Dickinson, B. C.; Miller, E. W.; Chang, C. J., A red-emitting naphthofluorescein-based fluorescent probe for selective detection of hydrogen peroxide in living cells. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2008, 18 (22), 5948-50. [pdf] [html]
9. Yoon, S.; Miller, E. W.; He, Q.; Do, P. H.; Chang, C. J., A bright and specific fluorescent sensor for mercury in water, cells, and tissue. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2007, 46 (35), 6658-61. [pdf] [html]
8. Miller, E. W.; Tulyathan, O.; Isacoff, E. Y.; Chang, C. J., Molecular imaging of hydrogen peroxide produced for cell signaling. Nat Chem Biol 2007, 3 (5), 263-7. [pdf] [html]
7. Miller, E. W.; Chang, C. J., Fluorescent probes for nitric oxide and hydrogen peroxide in cell signaling. Curr Opin Chem Biol 2007, 11 (6), 620-5. [pdf] [html]
6. Miller, E. W.; Bian, S. X.; Chang, C. J., A fluorescent sensor for imaging reversible redox cycles in living cells. J Am Chem Soc 2007, 129 (12), 3458-9. [pdf] [html]
5. Zeng, L.; Miller, E. W.; Pralle, A.; Isacoff, E. Y.; Chang, C. J., A selective turn-on fluorescent sensor for imaging copper in living cells. J Am Chem Soc 2006, 128 (1), 10-1. [pdf] [html]
4. Miller, E. W.; Zeng, L.; Domaille, D. W.; Chang, C. J., Preparation and use of Coppersensor-1, a synthetic fluorophore for live-cell copper imaging. Nat Protoc 2006, 1 (2), 824-7. [pdf]
3. He, Q.; Miller, E. W.; Wong, A. P.; Chang, C. J., A selective fluorescent sensor for detecting lead in living cells. J Am Chem Soc 2006, 128 (29), 9316-7. [pdf] [html]
2. Miller, E. W.; Albers, A. E.; Pralle, A.; Isacoff, E. Y.; Chang, C. J., Boronate-based fluorescent probes for imaging cellular hydrogen peroxide. J Am Chem Soc 2005, 127 (47), 16652-9. [pdf] [html]
1. Heasley, V. L.; Fisher, A. M.; Herman, E. E.; Jacobsen, F. E.; Miller, E. W.; Ramirez, A. M.; Royer, N. R.; Whisenand, J. M.; Zoetewey, D. L.; Shellhamer, D. F., Investigations of the reactions of monochloramine and dichloramine with selected phenols: examination of humic acid models and water contaminants. Environ Sci Technol 2004, 38 (19), 5022-9. [pdf]